Towards a Holistic Traffic Management System with Multi-Agent AI
As the backbone of a future-ready digital railway network, an intelligent traffic management system must be capable of planning and controlling train operations with unprecedented speed and precision. In our latest research, the Capacity & Traffic Management System (CTMS) department of Digitale Schiene Deutschland (DSD) presents a pioneering approach that harnesses an AI-Model trained with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) to generate detailed schedules for both planning and real‐time dispatching tasks.
A New AI-Based Approach to Traffic Management
Highly efficient rail operations require complex decision-making across vast network areas—where even small delays can have significant ripple effects. Traditional optimization methods, while robust, often require computation times that grow exponentially with increasing traffic density. Our new MARL approach offers a transformative solution. Built on the principles of Deep Reinforcement Learning, MARL trains an AI model to make individual, parallel decisions for each train. In doing so, it directly “steers” trains through a microscopic simulation of the railway system, taking into account everything from network topology and vehicle characteristics to the constraints of the safety system.
Using a detailed simulation environment that replicates real operational conditions, the AI learns through thousands of simulated runs. At each time step, it adjusts speed and sets the next target point for each train—effectively constructing an entirely new schedule. This constructive method not only uses all available degrees of freedom but also ensures that decisions made for one train are harmonized with the needs of the other trains in the network.
Method and Evaluation in Realistic Scenarios
The new MARL system was rigorously evaluated on a real section of the German railway network centered around Magdeburg central station. Two key use cases were addressed:
-
Dense Station Coordination: In scenarios focusing on a single, busy station, the MARL approach achieved a 100% success rate by flawlessly coordinating the entry, exit, and traffic stops of multiple trains in a confined space.
-
Network-Wide Planning and Dispatching: On a larger scale, encompassing mixed-traffic conditions with up to 41 trains per scenario, the system maintained success rates of 94%—even when unexpected disruptions forced trains to be rerouted.
Crucially, the computation times for generating these detailed schedules remained consistently below 30 seconds across various scenarios.
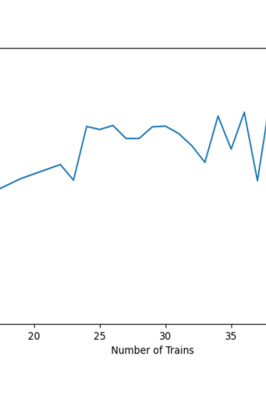
The linear increase in computation time with the number of trains marks a significant improvement over classical methods, which typically see an exponential growth in solution time. Already for scenarios with 35 trains, classical methods need over one hour for processing. In essence, the MARL approach not only produces high-quality schedules but does so with a speed that makes it highly applicable for real-time operations.
Summary and Outlook
Our research demonstrates that by combining state-of-the-art AI with a realistic simulation of railway operations, it is possible to overcome the limitations of conventional optimization methods. The MARL-based traffic management system is a promising candidate for the next generation of digitalized railway networks. With its ability to generate highly detailed, conflict-free schedules rapidly and its inherent scalability, this technology is set to transform how we plan, coordinate, and control train operations—even in the face of increasing traffic demands and unexpected disruptions.
As we continue to refine this approach—enhancing both its scalability and decision quality—the vision of a fully automated, adaptive, and efficient railway system comes ever closer to reality.
Further details to this new approach and test scenarios can be found in this publication.