CLUG
The CLUG project (Certifiable Localization Unit with GNSS) is investigating the extent to which the GNSS global satellite navigation system can contribute to train detection and be integrated into the current standard (ERTMS - ERTMS/ETCS - European Train Control System).
Project duration
Our partners














Localization of trains based on satellite navigation - the CLUG and CLUG 2.0 projects
Knowing the position of every train in real time is an important requirement for the rail system of the future. This is because precise and reliable localization is required for fully automated, driverless driving or for train operation in flexible headways (so-called moving blocks). Only when the trains run at optimized and dynamic intervals will the capacity of the rail network be increased. The current solution for localization is still based on trackside infrastructure elements (e.g. balises). The so-called CLUG project (Certifiable Localization Unit with GNSS) is investigating the extent to which the global satellite navigation system GNSS can contribute to train detection and be integrated into the current standard (ERTMS - ERTMS/ETCS - European Train Control System).
The CLUG project is driving forward sustainability, interoperability and digitalization in the rail sector. The use of GNSS for localization in rail transport is a game changer for the European Green Deal. The vision of the CLUG project is to bring train localization into the digital age. This is done by using a multi-sensor approach (GNSS as a key technology) in combination with digital maps. This will enable innovative concepts such as highly and fully automated driving (GoA2 and GoA4) or an intelligent traffic management system. The standardization of corresponding interfaces allows a modular design of the components on board the train. In conjunction with the reduction of trackside infrastructure, this leads to a reduction in costs and an increase in the reliability and quality of rail operations.
Objectives of the CLUG project (stage 1):
- Definition of mission requirements for localization
- Definition of a modular architecture
- Demonstration of the feasibility of a multi-sensor approach for localization
- Proof of concept for the algorithm used
The CLUG project (stage 1) took place from 2019 to 2022. It was funded by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) and financed as a European HORIZON 2020 project. The CLUG consortium consisted of various partners: railroad companies (SNCF, DB Netz AG and SBB), the signaling industry (CAF and Siemens), navigation experts (Airbus Defence and Space, Naventik, FDC), research institutes (ENAC) and certification experts (Navcert). As part of the Digitale Schiene Deutschland (DSD) sector initiative, DB Netz AG worked with these partners in the form of a cooperation project.
CLUG 2.0 was launched at the beginning of 2023 as a continuation of CLUG (stage 1). An expanded consortium (SYNTONY, RINA-C) will work on realizing the CLUG vision during the 24-month term.
Objectives of CLUG 2.0:
- Perform a RAMS analysis (Reliability, Availability, Maintainability & Safety)
- Demonstrate the localization unit in real time
- Extend the architecture with new functions
- Complete the high-level user requirements for the localization system
The challenge of real-time localization of trains
Today, the safety-relevant localization of trains is based on trackside infrastructure elements for track vacancy detection, such as balises and axle counters. They are installed at fixed headways along the railroad line. For the realization of so-called moving blocks in accordance with the ETCS standard, the train will in future communicate its relative position in relation to a reference point (balise) in the track. This position is determined with the help of odometry sensors on board the train (e.g. wheel revolution counters or Doppler radar). Information on train integrity (train integrity) is also required.
However, the trackside infrastructure is prone to failure and its maintenance is associated with high costs. Furthermore, deficits in the accuracy of odometry systems have a negative impact on rail operations. To improve the accuracy and data quality of localization information and reduce trackside infrastructure elements, the use of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) will help to solve this problem. This is the view of organizations such as the European Railway Agency (ERA). This is why the focus of the CLUG funding project is on this technical solution. If the project results are positive and this technology is used throughout Europe in the future, expensive infrastructure elements can be reduced. The use of GNSS has a positive impact on the reliability and operating costs of rail employees.
The CLUG approach
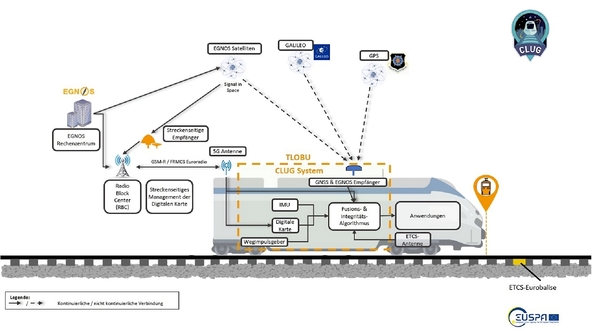
The train localization system in the CLUG project uses data from on-board GNSS sensors, inertial measurement units (IMU) and speed sensors as well as data from a digital map. The latter provides the line topology and the absolute reference points. The new localization system requires hardly any information from trackside infrastructure elements.
In addition to GNSS (a combination of GPS and Galileo), the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) is used in the central navigation system. It sends correction data that improves the security and performance of GNSS localization. The intelligent merger algorithm of the localization system combines all available information and sensor data and outputs the desired parameters such as position and speed with the corresponding integrity.
Further information:
https://digitale-schiene-deutschland.de/en/news/2022/CLUG-Train-Localisation-GNSS
-
GNSS is a technology that is integrated into the ERTMS (ERTMS). It can improve the accuracy and performance of train-side localization. This is necessary for future digital rail applications (fully automated driving, moving blocks, etc.).
-
On-board localization reduces the number of trackside infrastructure elements that are prone to failure, thereby reducing downtime and operating costs. At the same time, it increases reliability.
-
A Europe-wide standard for train detection is created with all the benefits of a common European railroad area.
CLUG (Stage 1):
- Identification of the needs, objectives and functional and performance requirements for the localization system using a top-down approach by the railroad undertakings, i.e. by the users of the system
- Definition of the system architecture and development of a prototype algorithm for a GNSS-based multi-sensor fusion method for localization in the railroad sector
- Development of procedures, methods and tools for the certification of the localization system
- Demonstration of the feasibility of the multi-sensor fusion method using data recorded during test runs in Germany, France and Switzerland.
CLUG 2.0:
- Revision of the system definition of the localization system and the requirements for the system
- Safety analysis of the localization system
- Development and design of the localization system
- Carrying out test drives and measurements
Results of CLUG (Stage 1, 2019 - 2022):
- Primary draft of a vehicle-side design with specification in a European framework
- Testing of two solution approaches. Both showed promising results in terms of along-track localization and speed determination
- Demonstration of the feasibility of a multi-sensor approach for localization
- Definition of a format for the digital map
The CLUG project was completed in May 2022. The final event took place on May 19, 2022 in Paris. A CLUG online webinar was held on June 9, 2022 to share the results virtually with the general public. The agenda and the recording of the online event can be found in the video:
Project CLUG 2.0 (2023-2025)
- Definition of higher-level user requirements, system requirements, operational scenarios
- Start of RAMS analysis
- Start of system definition of the localization system
- Preparation of test execution
Goals of CLUG 2.0:
- Performing a RAMS analysis
- Demonstrating the localization unit in real time
- Extending the architecture with new functions
- Completing the high-level user requirements for the localization system