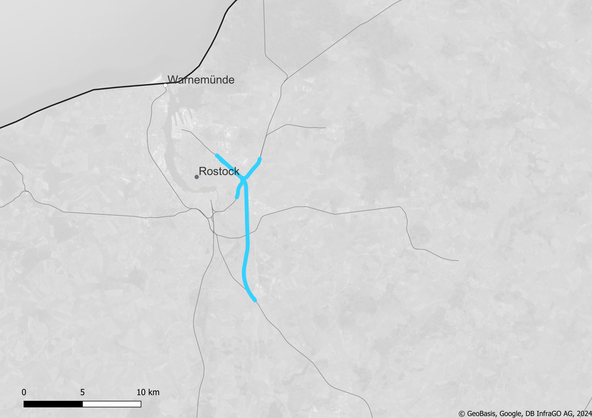
Rostock seaport – Kavelstorf gap closure
In order to enable consistent interoperability of control and safety technology in rail freight transport, the Rostock seaport – Kavelstorf section is being equipped with ETCS. This is an ETCS gap closure between the Rostock – Berlin line and the Rostock seaport.
Project duration
Route data
| Line from | Rostock seaport |
|---|---|
| Line to | Kavelstorf |
| Kilometers of line to be equipped | 22 km |
| Route number(s) | 6322, 6443, 6448, 6925 |
Planned actions
| ETCS | Level 2 with signals |
|---|---|
| Interlocking(s) | 1 ESTW-Z |
| Scope of equipment |
|
| Planned speed | 120 km/h |
Technologies
Contact
Disclaimer
The dates shown are legally non-binding forecasts based on the current status. The forecasts are in no way intended to establish any kind of legal claim whatsoever that completion will take place by the specified date and that use will be possible. For these reasons, the information should also not be used to make or prepare business decisions, for example, but not conclusively, with regard to the vehicle equipment or the compatibility between the vehicles and the infrastructure. If you have any questions, particularly regarding technical network access or obtaining binding information, please contact your customer advisor.
Most of the infrastructure projects are still in the planning phase, which means that the information provided on these pages reflects the current planning status and is updated regularly.
With the definition of Trans-European Transport Network corridors (TEN-T corridors), the aim is to standardise transport systems across Europe. On the railways, this primarily concerns the standardised conversion of routes to the European Train Control System (ETCS) in order to establish trans-European interoperability.
The TEN Orient/East-Mediterranean and Scandinavian-Mediterranean corridors, which connect Scandinavia with major conurbations in Germany and south-east Europe, run along the route to be upgraded. They also connect Germany's largest Baltic Sea port to the Rostock – Berlin route. Goods are shipped from the Rostock seaport to Trelleborg (Sweden) and Helsinki (Finland), among other destinations, by the fastest route. The route thus makes an important contribution to freight transport via the intra-European rail network.
The project is part of the European Deployment Plan (EDP) and a project of Digitale Schiene Deutschland. It envisages equipping the Rostock Seaport – Kavelstorf line with ETCS Level 2 with signals (ETCS L2mS). As German train control system "Punktförmige Zugbeeinflussung" (PZB) will be retained in addition to the signals, vehicles without ETCS equipment can continue to use the line. In conjunction with the "Rostock – Berlin line upgrade" (SeRoBe project), consistent ETCS operation from Rostock seaport to Berlin is to be made possible.
In order to fulfil the technical requirements for the ETCS equipment, the old relay interlockings (RSTW) in Rostock's seaport will first be replaced by a modern interlocking. In this case, a modern interlocking control centre with local operation will be built. In addition to a comprehensive optimisation of the track plan in Rostock's seaport, the new interlocking will be built in advance of this measure as part of the "Future Infrastructure Rostock Seaport" (ZIRS) project.
The line can then be equipped with ETCS. For this purpose, balises are attached to the sleepers at regular intervals. With the construction of an ETCS Radio Block Centre (RBC), new interfaces to the interlocking will also be implemented. ETCS stop markers must be attached to the existing signalling screens to replace the conventional signals in ETCS operation. Particular effort will be required to ensure ETCS entry and exit at the Rostock seaport. ETCS operation is to be enabled up to the entry group of the marshalling yard. Shunting will then take place there without train protection.
Bauende Bahn
This is a Deutsche Bahn project. We are building. So that people can build on us again. More information about the Bauende Bahn can be found here (in German only).